The Future of Manufacturing: Exploring the 3D Robo Printer
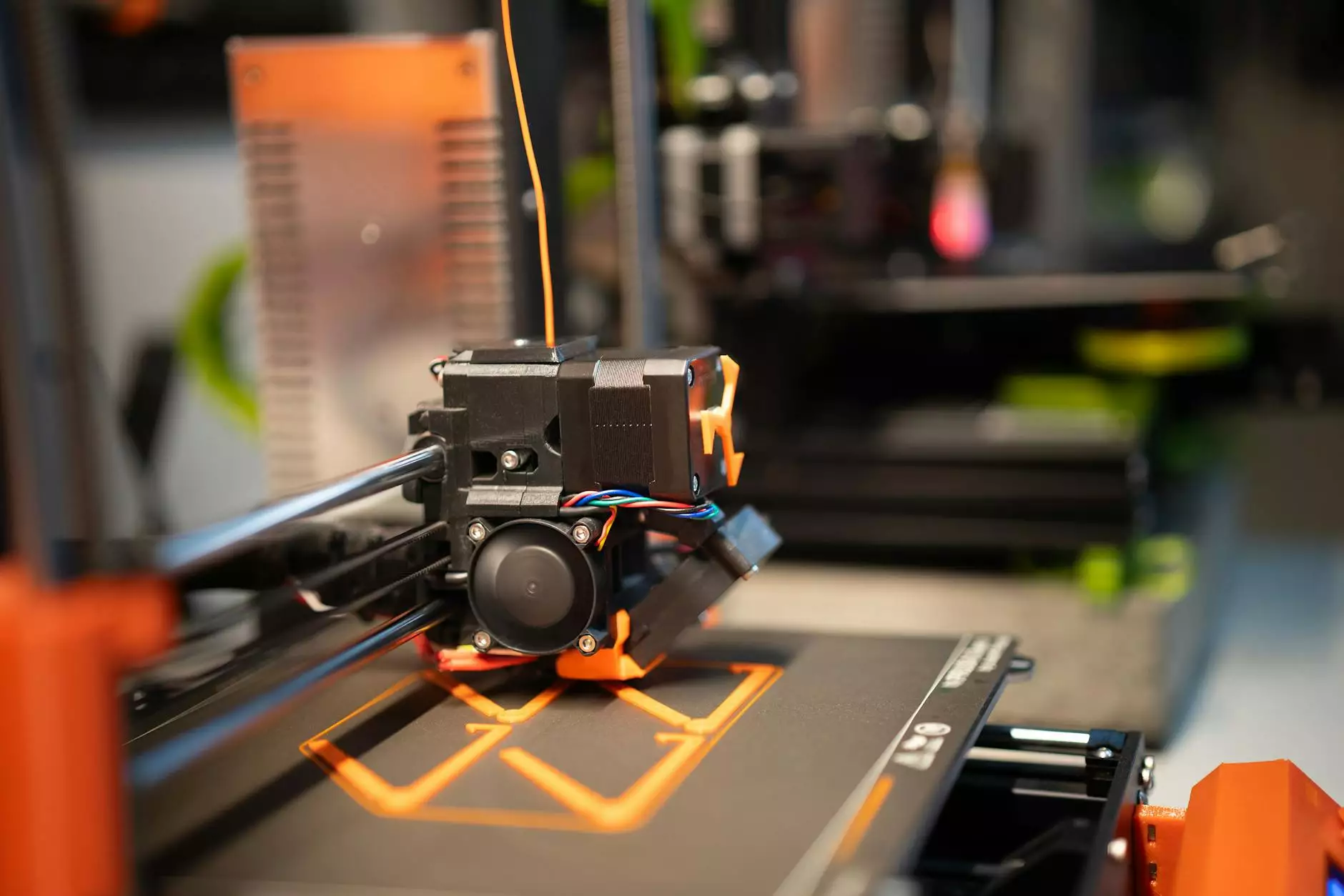

In the ever-evolving arena of technology, few innovations have had as profound an impact on manufacturing and design as the 3D robo printer. This remarkable apparatus merges advanced robotics with cutting-edge 3D printing technology, allowing for unprecedented levels of creativity, customization, and efficiency. As businesses strive to enhance their production capabilities, the need for versatile tools such as the 3D robo printer has never been more crucial. This article delves into the mechanisms, advantages, and implications of this groundbreaking technology, offering insights into how it is shaping the future of manufacturing.
Understanding the 3D Robo Printer
The 3D robo printer is a sophisticated device that combines traditional 3D printing techniques with robotic automation. At its core, it uses additive manufacturing, a process where materials are added layer by layer to create a three-dimensional object based on digital blueprints. This integration of robotics facilitates enhanced movement and precision, allowing for the fabrication of complex designs that were previously unattainable.
How Does a 3D Robo Printer Work?
The operational framework of a 3D robo printer involves several key components:
- Extruder Nozzle: The component that melts and extrudes the material.
- Build Plate: The surface upon which the printed objects are built, typically heated to prevent warping.
- Robotic Arm: Enhances movement capabilities, allowing for multi-directional printing.
- Control Software: Programs that convert 3D models into machine-readable instructions.
The printer begins its process by adhering to a precise set of coordinates derived from a 3D model. The robotic arm then maneuvers to deposit the materials accurately, layer by layer. This not only increases the speed of production but also significantly augments the complexity of the designs that can be achieved.
Benefits of Using a 3D Robo Printer
The implications of adopting a 3D robo printer in various sectors are vast. Here are some of the notable benefits:
1. Enhanced Customization
One of the standout features of the 3D robo printer is its capability for customization. In industries such as healthcare, personalized medical implants can be produced to match the unique anatomy of patients, improving the outcomes of surgeries and treatments.
2. Reduced Waste
Traditional manufacturing processes often involve significant material waste due to subtractions from larger blocks of material. In contrast, the additive nature of 3D printing minimizes waste by using only the material necessary to create the object. This aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices and reduces production costs.
3. Increased Speed of Production
The integration of robotics allows the 3D robo printer to produce items at a much faster pace compared to conventional methods. Rapid prototyping and shorter lead times enhance overall productivity and allow businesses to respond more rapidly to market demands.
4. Versatility of Materials
Modern 3D robo printers are compatible with a plethora of materials, including plastics, metals, ceramics, and even biological materials. This versatility opens up a myriad of possibilities across diverse industries, from aerospace to automotive, and from consumer products to medical devices.
Applications of the 3D Robo Printer
The applications of 3D robo printers span various sectors, demonstrating the technology's adaptability and potential:
1. Healthcare
In the medical sector, a 3D robo printer can create bespoke prosthetics, dental implants, and surgical models that enable surgeons to plan and practice complex procedures in advance. Furthermore, bioprinting is emerging as a method for fabricating human tissues, paving the way for advancements in regenerative medicine.
2. Aerospace
The aerospace industry benefits immensely from the use of 3D robo printers, which are able to manufacture lightweight yet strong components that enhance the performance of aircraft. This not only contributes to fuel efficiency but also improves overall safety through precision engineering.
3. Automotive
Automakers utilize 3D robo printers for rapid prototyping and production of complex parts, allowing them to test designs and iterate quickly. This not only shortens the product development cycle but also allows for customization according to consumer preferences.
4. Consumer Goods
In the consumer goods sector, companies are leveraging 3D robo printers to produce tailored products, ranging from unique home decor to personalized fashion items. This level of customization appeals to modern consumers who value individuality in their purchases.
Economic Implications of 3D Robo Printing
The economic landscape is being reshaped by the introduction of 3D robo printers. They are revolutionizing supply chains, reducing dependency on complex logistics, and enabling localized production. Businesses can now respond faster to market needs while minimizing the costs associated with shipping and warehousing.
Job Creation and Transformation
While automation often raises concerns about job displacement, the rise of 3D robo printers can lead to the creation of new job opportunities. Skilled positions focusing on design, programming, and maintenance of these sophisticated systems are on the rise. Additionally, the demand for training programs that teach these new skills is also increasing.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the advancements and benefits, several challenges remain for the widespread adoption of 3D robo printers. These include:
1. Material Limitations
While the range of compatible materials is expanding, the selection is still limited compared to traditional manufacturing methods. Research and development into new printing materials are crucial to unlocking further applications.
2. Regulatory Hurdles
In industries such as healthcare, regulatory approvals for new 3D-printed products can be time-consuming and complex. Establishing standardized guidelines for the use of 3D robo printers is essential for fostering innovation while ensuring safety and efficacy.
3. Intellectual Property Issues
The ability to replicate products with precision raises concerns about intellectual property rights. As 3D robo printers become more common, navigating the legal landscape concerning design copyrights will be paramount.
The Future Outlook
Looking ahead, the future of 3D robo printers appears bright. Continuous advancements in technology are set to enhance the capabilities of these printers further. As research into materials progresses, and as new industries recognize the potential of additive manufacturing, the demand for 3D robo printers is expected to skyrocket.
Industry Collaboration
Cross-industry collaborations will play a crucial role in realizing the full potential of 3D robo printing. By partnering with research institutions, businesses can pioneer innovations that push the boundaries of what is possible in manufacturing.
Educational Initiatives
With the growth of 3D robo printing, educational institutions are beginning to adapt their curricula to include training on this technology. By preparing the next generation of engineers, designers, and manufacturers, we can ensure a skilled workforce ready to tackle the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 3D robo printer represents a monumental shift in the manufacturing landscape. Offering unparalleled customization, efficiency, and versatility, it is transforming practices in industries from healthcare to aerospace. While challenges exist, the trajectory of this technology is undoubtedly pointing towards a future filled with potential. By embracing this innovation, businesses can not only optimize their production processes but also deliver products that cater to the increasingly personalized demands of consumers. Now is the time for companies to invest in 3D robo printing technology and harness its power to redefine the future of production.